Join us at AGG1, St Louis, MO - America's Center Convention Complex: 25-27 March
Consistent and clear maintenance processes are important for most of your assets, however, for heavy equipment it becomes critical. Not only does a systematic maintenance strategy help ensure longevity and optimal performance in heavy equipment, but it also minimizes the risk of accidents and breakdowns. This post covers the distinct characteristics of heavy equipment maintenance and how it can reduce costs and increase availability and productivity when done right. Above all, it will increase on-site safety and contribute to fewer accidents and a safer work environment for all.
This article covers:
- What is considered Heavy Equipment in the Construction Materials Industry?
- Characteristics of Maintenance on Heavy Equipment
- How Preventive Maintenance Can Help Reduce Costs and Prevent Downtime
- Importance of Scheduling and Checklists
- Checkproof’s Solution for Preventive Maintenance on Heavy Equipment
What is considered Heavy Equipment in the Construction Materials Industry?
In the construction materials industry, heavy equipment will typically be some of the most expensive assets on site – and often the most complicated to maintain.
Heavy equipment or heavy-duty machinery is specifically constructed for heavy-duty tasks. Designed to operate on simple mechanical engineering, but with powerful force. Examples of heavy machinery can include the following:
- Tractors
- Crushers
- Loaders
- Conveyor Belts
Characteristics of Maintenance on Heavy Equipment
A successful heavy equipment maintenance strategy involves a range of activities designed to keep the machinery running safely, smoothly, and efficiently. It is important to bear in mind that there is usually a large health & safety aspect involved in the maintenance of heavy equipment. For example, when performing maintenance on wear-metal on crushers in a quarry, lifting plans and isolation procedures are required to ensure that the asset is securely locked off, preventing any accidental activation.
The process often referred to as Lock Out, Tag Out, Try Out (LOTOTO) is critical in this context. This procedure involves securing the machine’s power sources to ensure it cannot be powered on unexpectedly, much like locking car keys in a box for safety.
Ensuring that machines cannot be powered on inadvertently during maintenance performance is crucial in a diverse and potentially hazardous environment. Effective guarding is also essential; any points where two moving parts meet known as NIP points, or any fast-moving parts that could cause injury, must be enclosed and secured with tools.
Maintenance in quarries involves multiple steps and intricate processes. For example, the functioning of a crusher depends on various factors, including what is feeding it and where the output is going. External factors such as weather and ground conditions also play a significant role. Maintenance is expensive, so it must be done correctly, balancing preventative and reactive approaches.
While condition-based maintenance is ideal, it is typically available only in advanced sites. Retrofitting older sites with modern sensors, such as Shaeffler and HID Technology, can make condition-based monitoring more accessible, enhancing the overall efficiency and safety of quarry operations.
Keeping the list below top of mind is a good start for heavy equipment maintenance:
- Step-by-step guides: Heavy equipment maintenance is often a connected process consisting of a series of maintenance checks. To this end, having a step-by-step guide to connected maintenance routines that need to be checked off, is essential.
- Regular Inspections: Routine checks to identify and address potential issues before they escalate, ideally combined with condition-based maintenance.
- Lubrication and Cleaning: Ensuring all moving parts are properly lubricated and machinery is clean to prevent wear and tear.
- Timely Component Replacement: Planning when to replace worn or damaged parts to maintain equipment performance and avoid breakdowns.
- Calibration and Adjustments: Ensuring equipment is calibrated correctly and making necessary adjustments to maintain precision.
- Documentation: Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities for future reference and compliance with regulations.
How Preventive Maintenance Can Help Reduce Costs and Prevent Downtime
Preventive maintenance contributes to reduced costs and downtime by allowing for planned, rather than last-minute, labor and parts procurement. The approach leverages internal talent and schedules specialist visits, such as those from crusher fitters, at fixed times, in line with the company’s needs. By helping to avoid unexpected breakdowns, preventive maintenance ensures parts are available when needed, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity. In contrast, unplanned repairs on heavy equipment often lead to rushed and expensive solutions, with costs skyrocketing, due to last-minute, desperate requests. Moreover, equipment failures tend to cause cascading issues, potentially blocking chutes or other conveyor belts and, in the worst case, shutting down entire sites for extended periods.
The cost difference between proactive and reactive maintenance is substantial, making preventive, and condition-based strategies crucial for efficient and cost-effective operations.
Here are some ways preventive maintenance can help reduce costs and prevent downtime:
- Early Problem Detection: Identifying and addressing minor issues before they become major problems can save on expensive repairs and replacements.
- Increased Equipment Lifespan: Regular maintenance helps extend the life of equipment, reducing the need for costly replacements.
- Improved Efficiency: Well-maintained equipment operates more efficiently, leading to lower operational costs and energy consumption.
- Reduced Downtime: By preventing unexpected breakdowns, preventive maintenance ensures that equipment is available and operational when needed, minimizing production interruptions.
- Increased Availability and Productivity: By ensuring machines are always in optimal working condition, you can maximize operational uptime and make availability and productivity gains, ensuring stocks aren’t depleted.
Importance of Scheduling and Checklists
Maintenance tasks in a quarry can vary in frequency and detail, from daily quick checks to more comprehensive weekly and monthly inspections.
- Daily checks are typically brief, focusing on immediate, observable issues.
- Weekly checks might delve a bit deeper.
- Monthly inspections are thorough and resource intensive.
Striking a balance is crucial, especially in operations with tight profit margins. Over-allocating resources to maintenance can result in inefficiencies, such as dedicating a full-time person to these tasks daily, which might not be sustainable.
When the plant is not running, checks can include inspecting lubrication, ensuring grease levels are adequate, and verifying that bearings run smoothly. These tasks often require removing guards, which is only feasible when the machinery is idle. Conversely, while the plant is operational, inspections might focus on monitoring temperature, listening for unusual noises, and feeling for vibrations. Certain adjustments, like tuning conveyor belts, can only be made while the machinery is running, highlighting the need for continuous, real-time monitoring and maintenance.
Bearing the above in mind, effective maintenance on heavy equipment relies on thoughtful scheduling coupled with customized checklists for each type of equipment and routine.
Some immediate gains are:
- Consistency: Scheduling maintenance tasks ensures regular and consistent checks, which can mitigate oversight and neglect.
- Accountability: Customized checklists provide a clear outline of tasks that need to be completed and to whom they should be assigned, ensuring accountability. Coupled with CheckProof’s RFID tag function on heavy equipment, will minimize any shortcuts being taken.
- Efficiency: Well-planned schedules and checklists streamline the maintenance process, saving time and resources.
- Compliance: Following scheduled maintenance and checklist protocols will help meet regulatory and safety standards.
Heavy equipment assets are resource-intensive, so when evaluating maintenance management systems, managing these valuable assets is key.
The guide below can help clarify what you should be looking for.
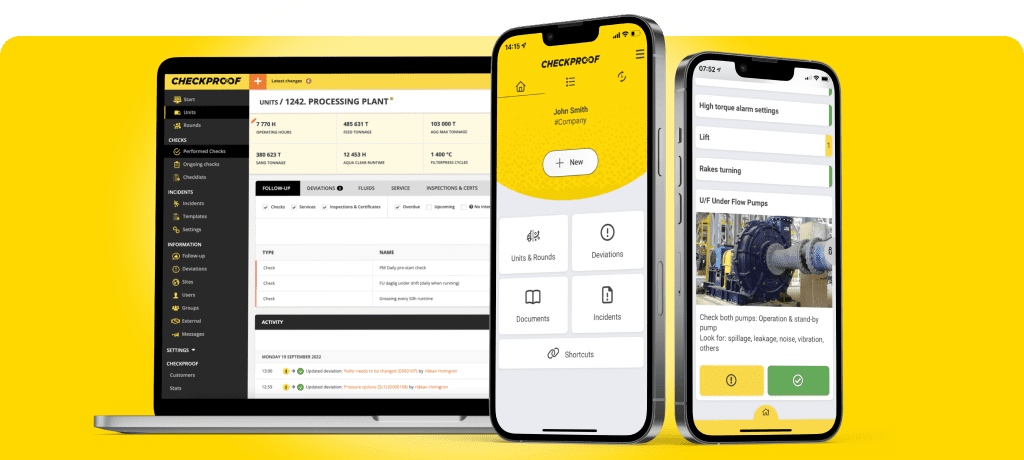
Checkproof’s Solution for Preventive Maintenance on Heavy Equipment
A complex maintenance routine requires a simple system for effective execution. CheckProof’s solution for preventive maintenance on heavy equipment includes a suite of digital tools, each serving a distinct purpose.
Planning Tool: A resource-management system that puts your calendar to shame. CheckProof’s Planning Tool helps you manage maintenance tasks and team members across sites from one place. With heavy equipment, there is a crucial need for agile operations. Automate scheduling of maintenance activities, with appropriate intervals and ensure tasks don’t fall behind, due to staff absence or other reasons. Often when analyzing root causes of heavy equipment failure, missed checks due to absent staff are a common culprit.
RFID Tag Scanning: This feature ensures that no area of the plant is overlooked, including those less frequented. RFID technology enables a quick scan of tags on your heavy equipment
Customized Checklists: Heavy equipment tends to come with a tome-like manual. With a mixed fleet, this can quickly become difficult to manage. With CheckProof, you can download the manuals onto the platform for easy access. You can also create customized checklists for troubleshooting manuals, giving step-by-step instructions until you’ve found the root cause.
Visuals & Mentions: You’re an operator in a remote part of the quarry – if you discover a repair that needs to be done, how quickly can you share it with management and assign it to colleagues? By uploading a video or photo, you can immediately share the state of your equipment to the right person.
Optimizing Fleet Performance: The lifespan of your fleet is dependent on running time, which affects everything from service intervals and leasing costs to second-hand value. So, to maximize the return on your investment, you need to optimize your running time. CheckProof’s Fleet Optimization feature ensures the setting of range odometers to automatically trigger inspections if limits are exceeded, removing guesswork and reducing operator stress. The feature also tackles idling time, through data and gamification.
Deviation triggers: The system’s telematics feature enhances visibility by generating deviation messages directly from machines whenever an issue arises. These messages can be categorized by severity: minor issues are directed to assistant managers, serious ones to managers, and health and safety concerns to the designated H&S personnel. This automated grading and notification system ensures accountability and prompt response, with defects immediately reported to the appropriate fitter or engineer, alleviating the burden on operators.
Intelligent Integrations: Every plant is different, and the state of their fleet can vary from truly advanced to decidedly old. What’s true for most sites, however, is that they will operate with a mixed fleet. CheckProof offers API and integrations so you can stream telematics data in real-time and get a true representation of your assets.
By incorporating Checkproof into your maintenance strategy, you can ensure that your heavy equipment is maintained proactively, efficiently, and in compliance with industry standards.
Want to know what CheckProof can do for you?
CheckProof's easy-to-use app makes it easier to do the right thing at the right time. Discover how you can run world-class maintenance that is both cost-effective and sustainable.

Maximize Efficiency with an OEE Monitoring System

Plant Asset Management Software:Maximizing Equipment Uptime

Machine Downtime Tracking: The key to smarter, more efficient operations

CMMS Software: What it is and why it’s key to First-Class Maintenance Operations

Revolutionizing Compliance: Banner Contracts on managing ISO audits with CheckProof

Implementation of Digital Systems: Rolling Out CheckProof Across Teams

Von Kraftstoffeinsparungen bis hin zu Produktionssteigerungen: Wie Cemex Deutschland erfolgreich CheckProof implementiert hat

A Recap of the CheckProof Industry Event & 10th Anniversary Celebration

Trend Report: Key moments in the Construction Materials industry (2014–2024)